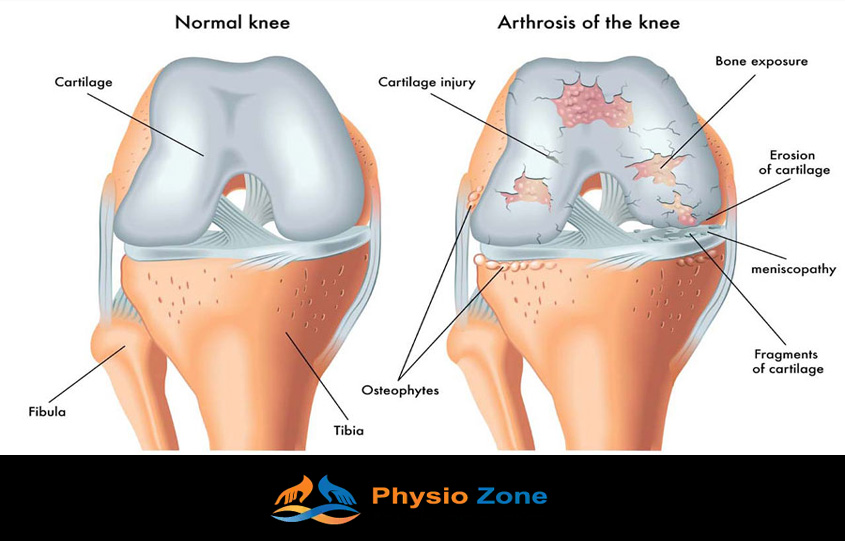
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people around the world and causes pain, stiffness, and less movement. There is no cure for osteoarthritis, but there are ways to control its symptoms and make life better for people who have it. Physiotherapy stands out as a useful and effective choice among these options. In this piece, we’ll talk about how physiotherapy can make a big difference for people with osteoarthritis.
Knowing about osteoarthritis
Before we talk about how physiotherapy can help, let’s take a moment to talk about what osteoarthritis is. Osteoarthritis happens when the cartilage that supports the ends of bones breaks down over time. This causes pain, swelling, and trouble moving the joints. The knees, hips, hands, and back are often affected.
Physiotherapy’s Role
Physiotherapy, which is also called physical therapy, is a non-invasive treatment that uses a variety of techniques to improve movement, reduce pain, and improve the way the body works as a whole. It’s a personalized treatment that can be changed to fit each person’s needs and limits. Here are some ways exercise can help:
- Managing pain: Pain is one of the hardest things about osteoarthritis. Physiotherapists use different methods to help relieve pain, such as manual therapy, ultrasound, and hot/cold treatment. They also teach patients exercises that help build muscles and keep joints stable, which can relieve stress on the joints.
- Exercises: It’s important to do the right exercises to deal with osteoarthritis. Physiotherapists come up with exercise plans that focus on stretching, building muscle, and keeping joints flexible. People often suggest low-impact activities like swimming, walking, and cycling because they help build muscle without putting too much stress on the joints.
- Increased range of motion: Joints with osteoarthritis can become stiff and have a limited range of motion. Physiotherapists use techniques like joint mobilizations and gentle stretches to improve joint flexibility and overall movement capacity.
- Functional Improvement: The final goal of physiotherapy is to help a person do everyday tasks more easily. Physiotherapists work closely with their patients to help them improve their ability to walk, climb stairs, or get in and out of a chair.
- Education and Self-Management: Physiotherapists teach their patients how to take care of themselves and teach them about their situation. This includes giving tips on posture, ergonomics, and ways to protect joints while doing daily activities, all of which help to make things better in the long run.
Other options for treating osteoarthritis
In addition to physiotherapy and exercise, there are a number of other ways to treat osteoarthritis, depending on the person’s needs and how bad the disease is.
1. Medication
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen can be bought over-the-counter or with a prescription. They lower pain and inflammation caused by osteoarthritis.
Analgesics: Over-the-counter painkillers like acetaminophen can help ease the pain of osteoarthritis, but they don’t do anything about the inflammation.
Drugs that make osteoarthritis worse (DMOADs): Still in the testing phase, these drugs are meant to slow the development of disease and protect cartilage.
2. Injecting
Corticosteroid Injections: When corticosteroids are injected directly into the damaged joint, they reduce inflammation and provide short-term pain relief.
Hyaluronic Acid shots: These shots are often used to treat knee osteoarthritis because they lubricate the joint and make it less painful.
3. Devices that help
Braces and Splints: Braces and splints are devices that help support and stabilize joints that are hurting. This reduces pain and stops further damage.
Canes or Walkers: Canes or walkers help people get around and relieve stress on their joints.
4. Keeping a healthy weight is important for managing osteoarthritis
especially in weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips. Joint stress can be greatly reduced by losing weight.
5. Changes to your way of life
Proper nutrition: A varied diet can help control inflammation and keep your joints healthy.
Physical Activity: Low-impact activities like swimming and yoga help joints work better without making pain worse.
Hot and Cold Therapy: Using heat or cold packs to relieve pain and stiffness for a short time.
6. Operations
Joint Replacement: When conservative methods don’t work, knee or hip replacement surgery may be an option.
Arthroscopy: With arthroscopy, damaged tissue or bone pieces are taken out of the joint with only a small amount of surgery.
7. Alternative treatments
Acupuncture: Some people find pain relief through acupuncture, which involves putting thin needles into certain spots on the body.
Herbal supplements: People think that supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin help keep joints healthy, but scientific evidence isn’t always clear.
Remember that these methods work differently for different people, so it’s important to talk to a doctor to make a personalized plan for managing osteoarthritis. They can give you advice about the best ways to improve your quality of life while you have this problem.
Conclusion
Physiotherapy is one of the most important parts of treating osteoarthritis as a whole. Physiotherapy helps people with osteoarthritis live more active and fulfilling lives by relieving pain, increasing mobility, and improving general function. If you or someone you care about is dealing with this condition, you might want to talk to a trainer about making a personalized treatment plan that can make a big difference in your health. Remember that being responsible today can make tomorrow easier and more mobile.